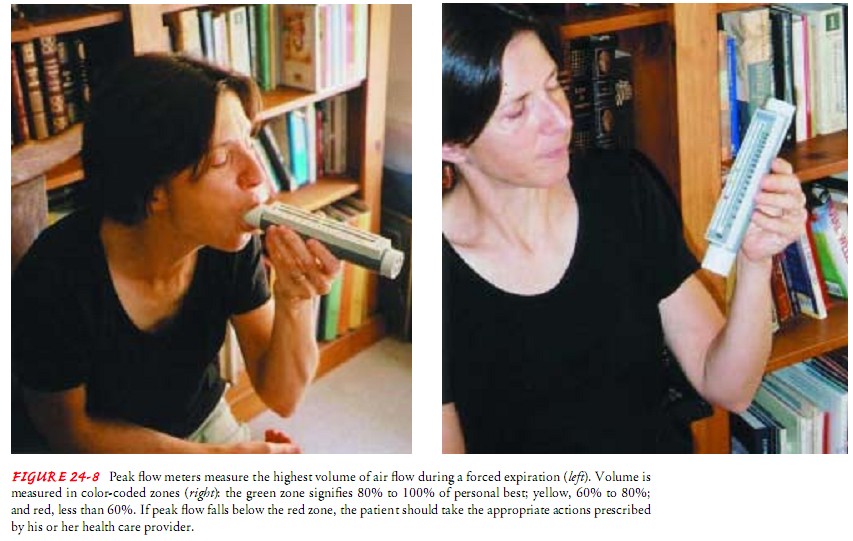
Status Asthmaticus
Definition
Severe and persistent asthma which does not respond to conventional therapy
Attacks last longer than 24 hours
Causes
Infection
Anxiety
Nebulizer abuse
Dehydration
Increased adrenergic blockage
Non specific irritants
Hypersensitivity to aspirin
Pathophysiology
Constriction of the broncholar smooth muscle
Swelling of the bronchial mucosa
Thickened secretions
Diameter of the bronchi decreases
Ventilation-perfusion abnormalit results in hypoxemia and respiratory alkalosis initiall followed by respiratory acidosis
PaO2 decreases
PaCO2 increases later causing respiratory acidosis
Clinical Features
Labored breathing
Prolonged expiration
engorgedneck veins
Wheezing
As the obstruction worsens, the wheezing disappears - a sign of impending respiratory failure.
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings
Pulmonary function studies - assess obstruction
ABG (Arterial Blood Gas measurement)
Respiratory alkalosis - low PaCO2
A rising PaCO2 frequently is a danger sign of impending respiratory failure
Medical Management
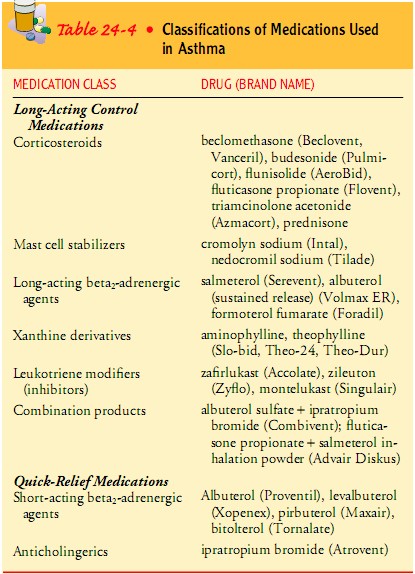
Short acting beta-adrenergic agonist & corticosteroids
O2 by Venturi mask or nasal catheter - PaO2 maintained at 65 to 85 mm Hg.
Sedatives contraindicated
Mechanical ventilation started - when the patient is tired
Nursing Management
Monitor skin turgor. SpO2
IV fluids 3 to 4 litres per day
Patient's energy needs to be conserved
Room quiet & free from respiratory irritants including flowers, tobacco smoke, perfumes or odours of cleaning agents
Non allergenic pillow